Electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes), battery-powered devices that provide nicotine and other additives to the user in the form of an aerosol, have become the most popular form of tobacco use among middle and high school youth. The recent National Youth Tobacco Survey, 2011-2018 found a distressing increase in the use of e-cigarettes, also known as “vaping“, that far surpassed the rate of use of conventional cigarettes during survey period.
What’s more, concurrent studies by both the Center for Tobacco Products at the Food & Drug Administration and the Centers for Disease Control point to a rapidly escalating problem. High school students currently using e-cigarettes increased from 1.5% in 2011 to 20.8% 2018. During 2017–2018 alone, e-cigarette use increased by 78% (from 11.7% to 20.8%).
At the same time, among middle school students, e-cigarette use increased from 0.6% in 2011 to 4.9% in 2018. During 2017–2018, current e-cigarette use increased by 48% (from 3.3% to 4.9%).
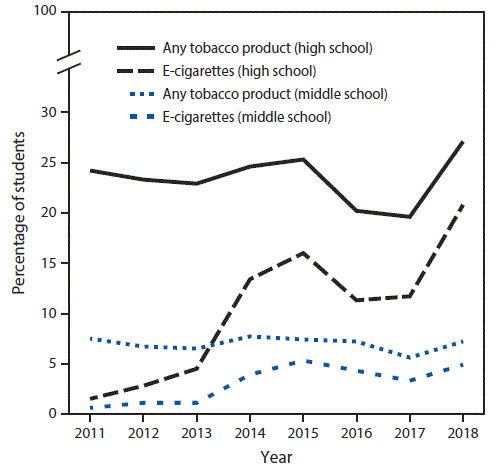
The studies also showed that, while current use of any tobacco product among high school students grew from 24.2% in 2011 to 27.1% in 2018, the use of e-cigarettes continued to increase at rates not seen in previous surveys.
This sharp rise in e-cigarette use among U.S. middle and high school students during 2017–2018 is likely because of the recent popularity of e-cigarettes shaped like a USB flash drive, such as JUUL. These products can be used discreetly, have a high nicotine content, and come in flavors that appeal to youth.
Although e-cigarettes can be of potential benefit to adult smokers as a complete substitute for smoking tobacco, adolescent use of any tobacco product, including e-cigarettes, is considered unsafe. The Surgeon General has concluded that “e-cigarette use among youths and young adults is of public health concern; exposure to nicotine during adolescence can cause addiction and can harm the developing adolescent brain”.
The Council on Recovery provides a wide range prevention and education programs aimed reducing tobacco use, especially among adolescents and young adults. These programs are provided at area schools, churches, community centers, employers, and health fairs. For more information about The Council’s Prevention & Education Programs , please call 713-942-4100, email education@councilonrecovery.org or contact us online.
